GitStack and other web servers
Wed, May 2, 2012
GitStack uses Apache to run its web administration interface and to handle git http connections.
However GitStack uses by default the port 80. You might have some issues to run some others webservers on the side (IIS, Apache, Wamp, etc).
Fortunately, GitStack provides a convenient way to change its port after the installation process.
This article will guide you on how to install GitStack on a computer which has an other webserver running on the port 80 (IIS in our case).
As GitStack runs by default on the port 80, you will have to stop your other webserver during the installation.
Install GitStack as usual following the Getting Started guide.
GitStack will be launched at the end of the installation.
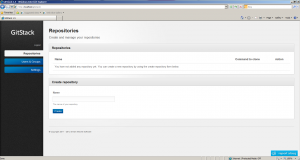
On the GitStack administration panel, open the Settings/General tab.
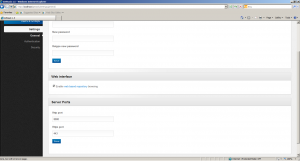
Modify the http port to another port (8080 for example) and click on save.
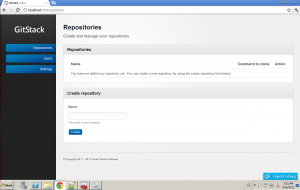
Reload your browser to http://localhost:8080/gitstack/
You can now restart your previous webserver (IIS in our example)
GitStack now runs on the port 8080. Make sure to clone and push on the port 8080 (ie : git clone http://192.168.0.2:8080/repo1.git )
However GitStack uses by default the port 80. You might have some issues to run some others webservers on the side (IIS, Apache, Wamp, etc).
Fortunately, GitStack provides a convenient way to change its port after the installation process.
This article will guide you on how to install GitStack on a computer which has an other webserver running on the port 80 (IIS in our case).
1. Stop IIS (or your other webserver)
As GitStack runs by default on the port 80, you will have to stop your other webserver during the installation.

2. Install GitStack
Install GitStack as usual following the Getting Started guide.
GitStack will be launched at the end of the installation.

3. Change GitStack’s port
On the GitStack administration panel, open the Settings/General tab.
Modify the http port to another port (8080 for example) and click on save.

Reload your browser to http://localhost:8080/gitstack/
4. You are done
You can now restart your previous webserver (IIS in our example)
GitStack now runs on the port 8080. Make sure to clone and push on the port 8080 (ie : git clone http://192.168.0.2:8080/repo1.git )


—————————————————-
Installation of another Apache web server with PHP.
—————————————————-
I had problems with this type of setup. Trying to install MantisBT with MySQL on Windows 7. Hopefully, this comment will be of use to someone.
Basically, after installing PHP GitStack won’t start up. The underlying problem:
* In the PHP installation directory, there is a libmysql.dll file that needs to be on the windows PATH…can’t remember why, but that’s a question for someone else
* Anyway, if the PHP installation directory is on the windows path, GitStack is unable to use it’s self contained installation of PHP and it stuffs up.
The workaround to start and use both servers:
* Copy libmysql.dll from C:\PHP (or your installation dir) to C:\PHP\workaround.
* Right-click My Computer -> Properties -> Advanced System Settings -> Environment variables
* Modify PATH: remove C:\PHP. Add C:\PHP\workaround.
Both servers should be usable now.
If you can easily change the port *after* installation, why isn’t there a mechanism for overriding this *upon install* instead of terminating any processes using port 80 *during* install?
Thanks.
Mainly because the installer is developed using nsis. Any modifications to the configuration files are very hard to handle.
I stopped IIS and there is no service to using port 80. I also checked with TCPView. But setup.exe still give port warning, and I couldn’t install your product. Why we don’t choose the port in installation steps?
Be advised: SQL Server Reporting Services (MSSQLSERVER) uses port 80 as well, and causes the install to be aborted!